Producer price indices - 1. quarter of 2005
Product Code: e-7032-05
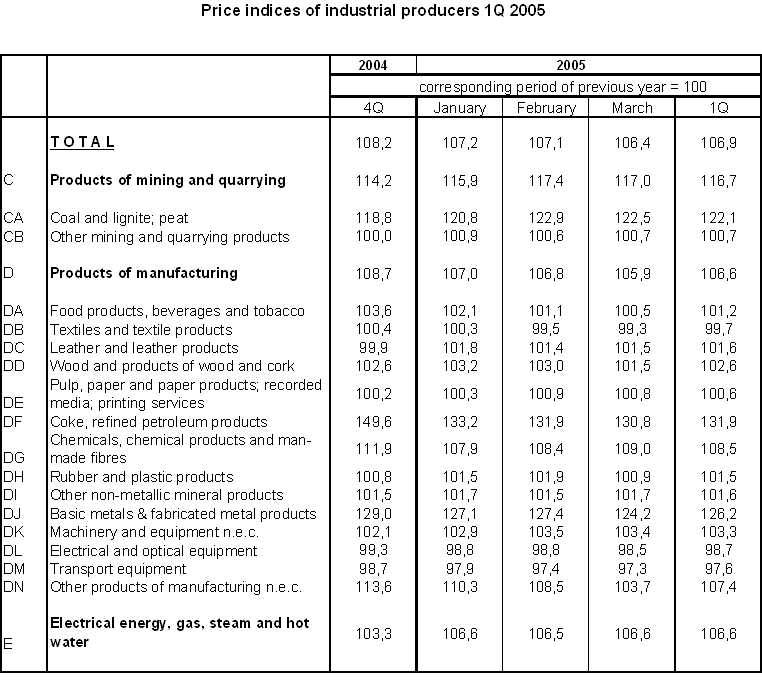
Producer price indices in the 1st quarter of 2005
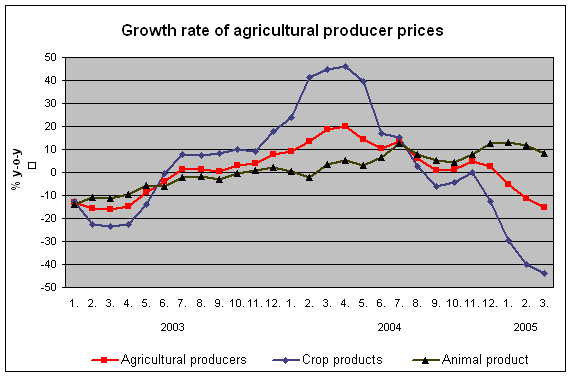
Agricultural producer prices fell sharply y-o-y in the 1st quarter of 2005; they recorded the first decrease since the 3rd quarter of 2003 (-10.8%, while they grew by 3.1% in the 4th quarter of 2004). Crop product prices fell by 39.2%, which was the highest y-o-y decrease since 1992 when indices began to be calculated in today’s way. Animal product prices rose by 10.9%.
The total drop in crop product prices was especially affected by lower prices of cereals by 28.4% (-13.0% in the 4th quarter of 2004). Significantly decreased prices of potatoes, which were down by 67.5%, vegetables by 48.7% (celery, parsley and onion) and fruit by 17.9% (apples).
The growth of animal product prices was mainly due to higher prices of cattle for slaughter by 19.0% (mainly prices of cows and calves), pigs by 30.2% (+15.6% in the 4th quarter of 2004) and milk by 6.2%. Only prices of eggs recorded a fall (-29.7%).
Industrial producer prices rose by 6.9% y-o-y. The main inflationary factors remained prices of coke, refined petroleum products and prices of basic metals and fabricated metal products. These two areas affected decisively the overall price level already in 2004 and their key importance continues also in the 1st quarter of 2005.
Prices of coke, refined petroleum products were by 31.9% higher y-o-y. Their growth reflects steep increases in prices and demand on world markets. The price of petroleum Brent oscillated around USD 45/barrel in January and February 2005 and exceeded USD 53/barrel in March (as against USD 30.34/barrel in February 2004).
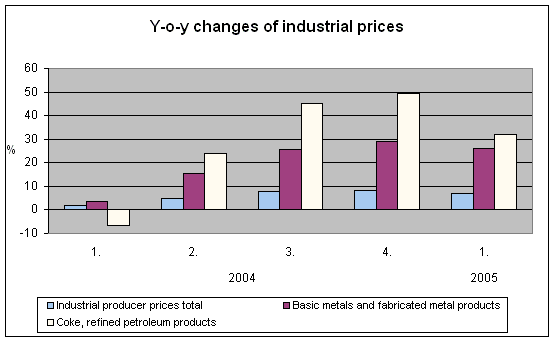
Prices of basic metals and fabricated metal products grew by 26.2% y-o-y. Particularly prices of iron, steel and ferro-alloys, which grew by 48.9% y-o-y on average in the 1st quarter of 2005, were at a high level. Related prices of other groups of products went up too. A considerable growth was recorded for prices of cast-iron and steel tubes and tube fittings (+37.2%) and prices of other first processed iron and steel (+39.8%). World demand for raw materials, metals and products thereof remains high and the prices on world markets rise. Import prices of input raw materials in the CR increased in this context. In January 2005, import prices of metal ores were by 67.8% higher y-o-y.
High price increases were recorded also for coal, lignite and peat (+22.1%), chemicals, chemical products and man-made fibres (+8.5%) and other manufactured goods n.e.c. (+7.4%).
Prices of food products, beverages and tobacco grew markedly slower than in 2004 (+1.2% in the 1st quarter of 2005, compared to +4.8% in the whole year 2004). The slowed down rate of growth was essentially affected by prices of grain mill products, starches and starch products (-4.0%), bread, fresh pastry goods and cakes (-0.5%) and prepared animal feeds (-9.8%). Price of the main input, i.e. food wheat, went down to CZK 2880/t in February 2005 (from CZK 4330/t a year earlier). Also price of fodder wheat dropped (to CZK 2520/t from CZK 3624/t, in the same period). World markets sold wheat considerably cheaper than a year earlier (-21.6% y-o-y in February 2005). Falling trend was recorded for consumer prices of cereals and bread, fresh pastry goods and cakes, which were by 1.1% lower y-o-y in February.
On the other hand, mainly prices of meat and meat products rose (+5.6%). Prices of both beef and pig meat were up. These prices reflected higher prices of agricultural producers of pigs for slaughter (+35.5% y-o-y in February). Prices of cattle for slaughter increased by 18.1%. Among individual areas of prices, consumer prices rose slowest. Prices of meat in the trade network increased by 2.4% y-o-y in February. As to other food, industrial producer prices of dairy products (+3.0%) and beverages (+4.2%, of which predominantly beer +7.7%) grew.
Of principal importance for all branches were higher prices of electrical energy, gas, steam and water by 6.6%, of which production and distribution services of electricity by 8.1%, water by 4.3% and steam and hot water supply services by 3.6%.
A long-term falling trend was observed for prices of electrical and optical equipment and transport equipment. On average for the 1st quarter of 2005, these prices were down by 1.3% and 2.4% y-o-y, respectively.
In comparison to the European Union , industrial producer prices in the Czech Republic grew faster y-o-y in 2005. They were by 7.1% higher y-o-y in February in the CR and by 5.0% in the EU25. Prices in some of the Member States increased faster than in the CR: most in Hungary (+10.0), the United Kingdom (+8.7%) and Luxembourg (+8.5%). They were by 2.1% higher in Slovakia. (All in February 2005.)
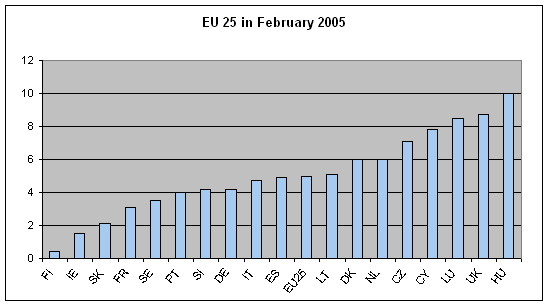
* February 2005 data for some countries were not available.
Construction work prices grew by 4.2% y-o-y in the 1st quarter of 2005 (4.3% in the 4th quarter of 2004), prices of construction material inputs rose by 8.0% (8.3% in the 4th quarter of 2004).
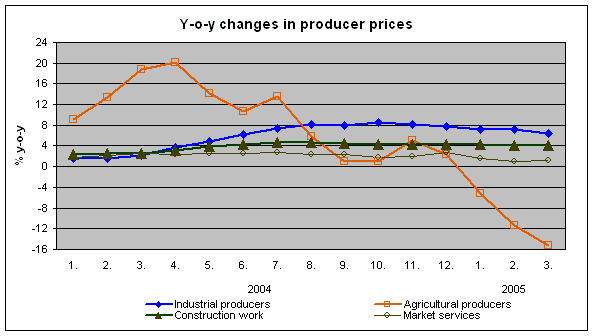
Y-o-y increase in market services prices slowed down to 1.3% in total in the 1st quarter of 2005 (from 2.2% in the 4th quarter of 2004). The decisive effect on the development of the overall price level had predominantly prices of real estate, renting and business services , which grew by 1.6% (+2.6% in the 4th quarter of 2004). In this area, mainly prices of advertising services (+2.7%) and prices of computer and related services (+6.8%) were up, on the other hand prices of real estate services (-0.8%) and prices of exhibition and fair service activities (-1.3%) dropped. Prices of financial intermediation services, except insurance and pension funding services, rose by 4.3% y-o-y in the 1st quarter of 2005, especially due to higher prices of monetary intermediation services (+8.0%); prices of leasing services fell (-1.7%). Prices in insurance and pension funding services, except compulsory social security services, were up by 0.6% (+1.9% in the 4th quarter of 2004). Prices of fire and other damage to property insurance services grew by 1.2%, prices of theft insurance services by 1.0% and prices of motor vehicle insurance services by 0.4%. Prices of post and telecommunication services were by 1.0% lower in total due to lower prices of mobile telephone services (-7.4%). On the other hand, prices of state post services rose by 10.4%. Prices of national freight transportation services grew by 1.4%. Prices of freight transportation services by road were by 2.6% higher.