External trade - 1. quarter of 2008
Product Code: e-6032-08
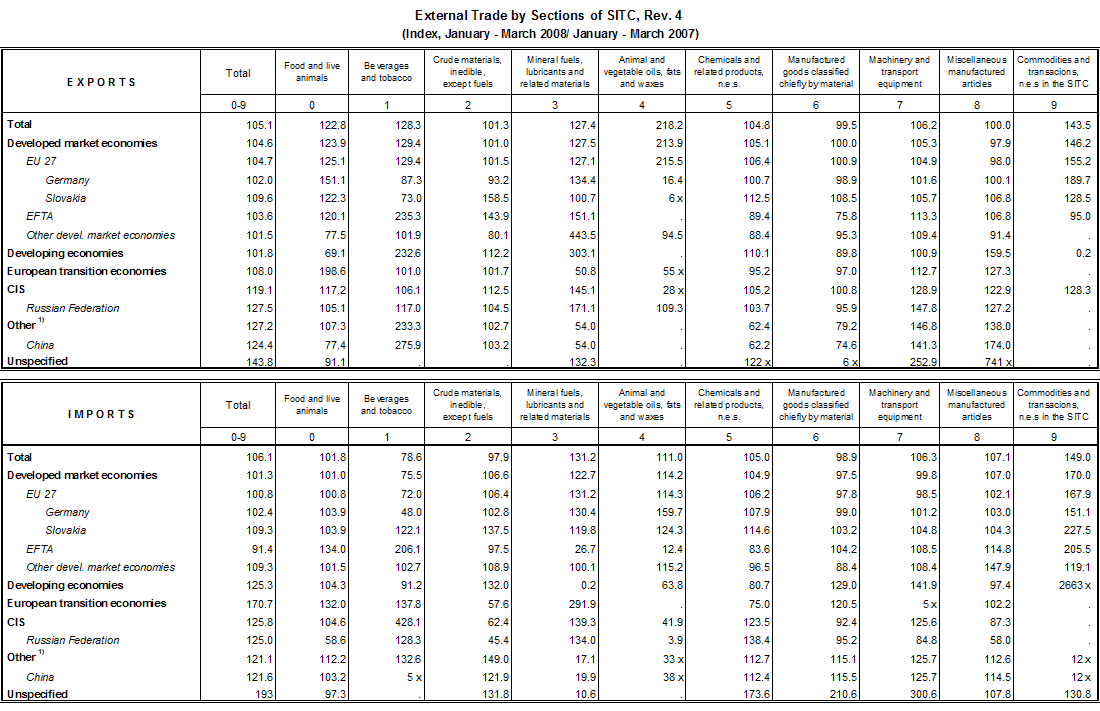
In Q1 2008 external trade 1 grew less year-on-year. External trade turnover grew by 5.6%. Both exports and imports recorded lower rates of growth; increase of exports was by 1.0 percentage point lower than increase of imports. The trade balance reached a CZK 34.6 billion surplus.
In the first quarter of 2008, in comparison to the first quarter of 2007:
- exports increased by 5.1% and reached CZK 631.9 billion, imports grew by 6.1% and reached CZK 597.3 billion. Increases in exports and imports accounted for 47.3% and 52.7% respectively of the year-on-year growth of external trade turnover. Due to appreciation of CZK against EUR and even more against USD 2 , exports and imports in these foreign currencies grew more rapidly – exports and imports in EUR by 15.4% and 16.5% respectively, exports and imports in USD by 32.0% and 33.2% respectively;
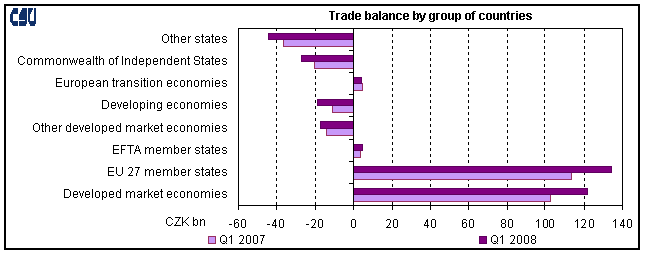
- trade balance surplus was by CZK 3.5 billion lower and reached CZK 34.6 billion (the rate of coverage of imports by exports was 105.8% in comparison to 106.8% in Q1 2007. By group of countries, trade surplus with EU27 states improved (by CZK 21.2 billion) and trade deficit with non-EU countries deteriorated (by CZK 24.7 billion). Trade surplus with EU27 states covered nearly 86% of the trade deficit with non-EU countries. The surplus with the European transition economies decreased by CZK 0.6 billion year-on-year, trade deficit deteriorated with the CIS 3 countries by CZK 6.5 billion, with other states 4 by CZK 7.6 billion and with developing economies by CZK 7.6 billion. By commodity section, trade balance improved year-on-year due to a CZK 5.3 billion increase of surplus in ‘machinery and transport equipment’, a CZK 0.6 billion increase of surplus in ‘manufactured goods classified chiefly by material’ and a CZK 5.0 billion decrease of deficit in ‘agricultural and food crude materials and products‘; trade balance deteriorated due to a decrease of surplus in ‘miscellaneous manufactured articles’ and a CZK 1.2 billion increase of deficit in ‘chemicals and related products’, and especially due to a 9.2 CZK billion increase of deficit in ‘crude materials, inedible, and mineral fuels’;
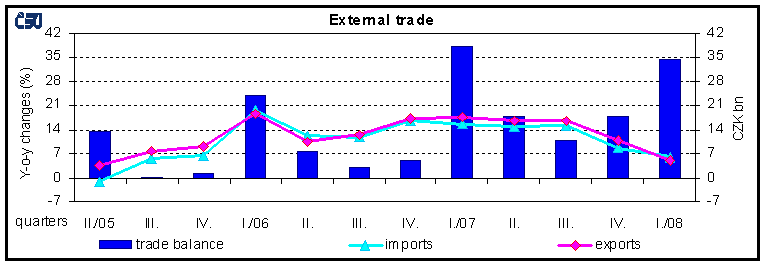
- by group of countries, the share of EU27 states in total exports slightly decreased (from 86.2% to 85.8%) and so did in total imports (from 71.9% to 68.3%). Higher shares in total exports were registered for CIS countries and other states, while the shares of the remaining groups of countries (except European transition economies) decreased. In total imports the shares of all the other groups of countries (except EFTA states) grew, in particular of CIS countries, developing economies and other states;
- by commodity section, mainly the share of ‘machinery and transport equipment’ in total exports rose (from 54.5% to 55.0%) to the detriment of ‘manufactured goods classified chiefly by material’ and ‘miscellaneous manufactured articles’. ‘Machinery and transport equipment’ maintained its share recorded in Q1 2007 (42.5%). With the exception of ‘crude materials, inedible, and mineral fuels‘, which raised their share in total imports from 10.5% to 12.2%, the shares of other sections of the SITC decreased.
In comparison to external trade of EU27 states and external trade of the new EU member states, the growth rate of external trade in the Czech Republic was better in Q1 2008. Data for January 2008 released by Eurostat on 17 April 2008 say that EU27 (EU15) exports rose by 8.4% (7.5%) and EU27 (EU15) imports by 9.7% (8.9%) on average year-on-year (based on EUR). Exports and imports of the twelve new member states were higher by 17.6% and 16.3% respectively on average year-on-year. In January 2008 the share of the twelve new member states in total EU27 exports increased to 10.6% (from 9.8% in January 2007) and their share in total EU27 imports grew to 11.4% (from 10.7% in January 2007). The EU27 trade balance reached a EUR 16.7 billion deficit in January 2008 (EU15 deficit was EUR 12.2 billion and the twelve new member states’ deficit was EUR 4.5 billion). As one of the few (9) EU member states and the only one among the new EU member states, the Czech Republic recorded a trade surplus in January 2008.
The external trade figures for Q1 2008 were affected by:
- growth of industrial production. In January–February 2008 the y-o-y industrial production index reached 110.2 (of which in manufacturing 110.7). Above-the-average year-on-year increases were recorded in ‘manufacture of electrical and optical equipment’ (25.6%), ‘manufacture of machinery and equipment’ (19.5%) and ‘manufacture of transport equipment’ (14.5%). The rise in manufacturing industries 5 had a favourable effect on export increase. Manufacturing exports made up 96.3% and increase in ‘manufacturing’ accounted for 89.2% of increase in total exports. Compared to Q1 2007, manufacturing exports grew by 4.7% (CZK +27.4 billion).
The most important section of manufacturing exports in Q1 2008 remained ‘machinery and transport equipment’, especially ‘road vehicles’, ‘electrical machinery, apparatus and appliances, n.e.s.’, ‘office machines and automatic data-processing machines’, ‘general industrial machinery and equipment’ and ‘telecommunications equipment n.e.s.’. Exports of ‘road vehicles’ made up 17.1% of total exports in Q1 2008 (17.7% in Q1 2007), of which exports of passenger cars was 8.6% (9.5% in Q1 2007) and exports of ‘parts and accessories for motor vehicles’ 7.1% (7.0% in Q1 2007). While external trade in road vehicles produced the highest surplus among all SITC classes, the surplus was by CZK 1.5 billion lower year-on-year, of which surplus in passenger cars fell by CZK 3.7 billion and surplus in ‘parts and accessories for motor vehicles’ grew by CZK 1.6 billion. The second largest surplus in machinery trade (by CZK 2.1 billion higher year-on-year) and in total external trade as well was registered for ‘general industrial machinery and equipment’;
- unfavourable terms of trade 6 . In January–February 2008, in comparison to January–February 2007, export and import prices were down by 3.8% and 2.5% respectively on average. The terms of trade figure reached 98.7. In the same period exports and imports increased by 11.2% and 10.9% respectively at current prices, but by 16.1% and 14.5% respectively at constant prices. In January–February 2008 prices lowered current price exports by nearly CZK 19 billion and current price imports by more than CZK 13 billion;
- economic slowdown in EU member states due to continuing instability in financial markets, slowdown in the US and growth of commodity world prices (especially food, oil and natural gas). According to a forecast of the European Commission, EU27 GDP will rise by 2.0% in 2008 (as against 2.8 in 2007). Economic development in two main trading partners – Germany and Slovakia – will be decisive for external trade of the Czech Republic. Germany was the destination for 30.9% and Slovakia for 8.6% of the Czech Republic’s total exports in Q1 2008 (as against 31.6% and 8.3% respectively in Q1 2007). Exports to Germany grew by 2.0% (CZK +3.8 billion) and to Slovakia by 9.6% (CZK +4.8 billion) year-on-year.
A more detailed view of external trade by group of countries in Q1 2008 shows that, in comparison to Q1 2007:
- exports to all groups of countries increased, individual rates varied considerably. Above-the-average relative growth was observed in exports to other states (China), CIS countries (the Russian Federation) and European transition economies. Yet in value the growth of exports to these groups of countries made up only 16% of the growth of total exports. Exports to other groups of countries grew below the average. Exports to EU27 states, which increased by CZK 24.5 billion year-on-year, made up nearly 80% of the absolute increase in total exports. The rise in exports to EU27 states reflected different growth rates of exports to individual EU27 member states. Exports to eleven EU27 member states increased more than the average – for example exports to Poland, Romania, Sweden, Slovakia, Italy and the United Kingdom; below-the-average increases were registered, e.g., in exports to Germany, the Netherlands, France and Spain; exports to, e.g., Hungary and Belgium decreased. The highest year-on-year increases in value were registered for exports to Slovakia (CZK +4.8 billion), Poland (CZK +4.3 billion) and Germany (CZK +3.8 billion). Exports to these states represented over 42% of increase in total exports and nearly 52% of increase in exports to EU27 states.
- imports from all groups of countries grew, except for imports from EFTA states (lower imports from Norway). Above-the-average increases were recorded in imports from European transition economies (the Russian Federation, Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan), developing economies (Thailand, Malaysia and Korea), other states (China) and other developed market economies (Japan). Unimportant relative growth was observed in imports from EU27 states. Increase (in absolute terms) in imports from EU27 states by CZK 3.3 billion made up only less than 10% of increase in total imports. Imports from eleven EU27 states grew more than the average – for example imports from Slovakia, Austria, Poland, Hungary, Germany and the United Kingdom; imports from the remaining 16 EU27 states stagnated or decreased year-on-year, for example imports from France, the Netherlands, Italy, Belgium, Sweden and Romania. Year-on-year increases of imports from Germany (CZK +3.9 Billion), Slovakia (CZK +2.7 billion and Austria (CZK +1.9 billion) were the highest.
- trade surplus with EU27 states grew by CZK 21.2 billion and deficit with the non-EU27 countries rose by CZK 24.7 billion. Trade deficit with the non-EU27 countries was mainly due to the trade deficit with other states that reached CZK 44.3 billion (the rate of coverage of imports by exports was 8.3% in Q1 2008 in comparison to 7.8% in Q1 2007), CIS countries (CZK 27.0 billion), developing economies (CZK 18.9 billion) and other developed market economies (CZK 17.2 billion).
The trade balance and year-on-year balance increases/decreases with individual groups of countries reflected the situation of external trade balance with the main partner states, as documented by the table below. External trade with twelve EU27 states reached a surplus of CZK 123.2 billion, of which trade surplus with three EU27 states (Germany, Slovakia and the United Kingdom) made up 55.6%. Trade balance with twelve non-EU27 states reached a deficit of CZK 100.3 billion, of which trade deficit with three states (China, the Russian Federation and Japan) made up CZK 83.0 billion.
Balance of trade with selected countries | |||||||
| EU27 member states | 2007 | 2008 | Y-o-y change | Non-EU27 states | 2007 | 2008 | Y-o-y change |
Q1 | Q1 | ||||||
CZK billion | CZK billion | ||||||
| Germany | 29.0 | 28.9 | - 0.1 | China | - 35.9 | - 43.5 | - 7.6 |
| Slovakia | 20.7 | 22.8 | 2.1 | Russian Federation | - 17.8 | - 22.0 | - 4.2 |
| United Kingdom | 15.6 | 16.8 | 1.2 | Japan | - 13.5 | - 17.5 | - 4.0 |
| France | 3.3 | 9.4 | 6.1 | Korea | - 3.7 | - 6.9 | - 3.2 |
| Romania | 4.6 | 7.5 | 2.9 | Thailand | - 2.8 | - 5.7 | - 2.9 |
| Austria | 8.1 | 7.4 | - 0.7 | Azerbaijan | - 4.1 | - 5.5 | - 1.4 |
| Belgium | 6.3 | 6.4 | 0.1 | Taiwan | - 5.9 | - 5.4 | 0.5 |
| Sweden | 4.4 | 5.8 | 1.4 | Malaysia | - 3.0 | - 3.4 | - 0.4 |
| Poland | 3.0 | 5.5 | 2.5 | Switzerland | 1.9 | 3.0 | 1.1 |
| Italy | 2.8 | 5.5 | 2.7 | United Arab Emirates | 2.9 | 2.4 | - 0.5 |
| Spain | 5.3 | 5.4 | 0.1 | Croatia | 2.1 | 2.1 | 0.0 |
| Hungary | 3.3 | 1.8 | - 1.5 | Ukraine | 1.5 | 2.1 | 0.6 |
Changes in the commodity structure of external trade in Q1 2008, in comparison to Q1 2007, were characterised in:
- machinery and transport equipment by slightly above-the-average growth of exports and imports. The share of ‘machinery and transport equipment’ in total exports grew from 54.5% to 55.0%, its share in total imports remained constant year-on-year (42.5%). Higher exports (imports) of ‘machinery and transport equipment’ by CZK 20.2 billion (by CZK 14.9 billion) accounted for 65.8% (43.6%) of increase in total exports (total imports). Surplus of trade in machinery and transport equipment reached CZK 93.6 billion (exports of machinery covered 36.8% of imports), the surplus with EU27 stood at CZK 127.7 billion. The highest surplus (yet by CZK 1.5 billion lower) was produced in trade in ‘road vehicles’, followed by ‘general industrial machinery and equipment’ (CZK +2.1 billion y-o-y), ‘office machines and automatic data-processing machines’, ‘telecommunications and sound-recording equipment’ and ‘machinery specialized for particular industries’;
- manufactured goods classified chiefly by material by decreasing exports and imports. The share of these goods in total exports and imports decreased (from 20.8% to 19.7% and from 21.6% to 20.2% respectively). The trade surplus grew insignificantly (CZK +0.6 billion) year-on-year. This improvement was due to deficit decreases in ‘iron and steel’ by CZK 1.7 billion and ‘non-ferrous metals’ by CZK 0.9 billion. The highest surpluses (though lower than in Q1 2007) were concentrated in ‘manufactures of metals’, ‘non-metallic mineral manufactures’ and ‘rubber manufactures, n.e.s.’;
- miscellaneous manufactured articles, commodities and transactions not classified elsewhere in the SITC by stagnating exports and above-the-average growth of imports, which resulted in a fall of surplus by CZK 4.0 billion year-on-year and decrease of their share in total exports and increase in total imports. Trade surplus dropped in ‘prefabricated buildings, sanitary, plumbing, heating and lighting fixtures and fittings, n.e.s.’ and in ‘furniture and parts thereof’. Trade deficit deteriorated in ‘articles of apparel and clothing accessories’, ‘footwear’ and ‘professional, scientific and controlling instruments and apparatus, n.e.s.‘;
- chemicals and related products by above-the-average increase of exports and imports and thus by stagnation of their share in total exports (5.8%) and total imports (10.5%). The deficit in these products was the second highest (CZK 25.9 billion) and rose year-on-year by CZK 1.2 billion. The large deficit (up by CZK 0.6 billion year-on-year) was concentrated in ‘medicinal and pharmaceutical products’. Trade deficit in ‘plastics in primary forms’ decreased year-on-year and trade deficit in ‘chemical materials and products, n.e.s.’ deteriorated;
- crude materials, inedible, and mineral fuels by highly above-the-average growth of exports and even more of imports, which resulted in a year-on-year increase in the share of these products in total external trade. Deficit of trade in these products grew by CZK 9.2 billion year-on-year and remained the highest (CZK 37.0 billion) among all sections of the SITC. Deficit deteriorated due to higher deficit in trade in ‘petroleum, petroleum products and related materials’ by CZK 7.3 billion and ‘gas, natural and manufactured’ by CZK 2.9 billion. In Q1 2008, compared to Q1 2007, imports of these commodity items grew by 36.3% and 26.3%. The increase (especially oil imports) was affected by growing prices due to world market prices. In Q1 2008, in comparison to Q1 2007, world prices 7 of crude oil Brent and natural gas were by 64.5% and 27.7% respectively higher. In volume, oil imports remained constant year-on-year and natural gas imports grew by nearly 24%. The balance of trade in crude materials, inedible, and mineral fuels was affected by increase in trade surplus in ‘coal, coke and briquettes’ and ‘oil-seeds and oleaginous fruits’ and decrease in trade surplus in ‘electric current’ and ‘cork and wood’;
- agricultural and food crude materials and products by the highest relative increase of exports and fall of imports. Trade deficit fell by CZK 5.9 billion year-on-year. Trade deficit decreased in ‘vegetables and fruit’ and ‘meat and meat preparations’; trade deficit rose in ‘dairy products and birds eggs’ and ‘cereals and cereal preparations’; trade balance of ‘tobacco and tobacco manufactures’ turned from deficit to a surplus.
External trade balance of products with the biggest effect on the overall trade balance in Q1 2008 | |||
Favourable effect | Adverse effect | ||
| Division of SITC, Rev. 4 | CZK billion | Division of SITC, Rev. 4 | CZK billion |
| 78 - Road vehicles | 55.1 | 33 - Petroleum, petroleum products and related materials | -28.9 |
| 74 - General industrial machinery and equipment | 12.0 | 34 - Gas, natural and manufactured | -16.8 |
| 69 - Manufactures of metals | 8.6 | 68 - Non-ferrous metals | -11.8 |
| 75 - Office machines and automatic data-processing machines | 7.2 | 54 - Medicinal and pharmaceutical products | -10.3 |
| 66 - Non-metallic mineral manufactures | 6.4 | 67- Iron and steel | -5.8 |
| 62 - Rubber manufactures | 5.7 | 57 - Plastics in primary forms | -4.9 |
| 82 - Furniture, and parts thereof | 5.6 | 05 - Fruit and vegetables | -4.6 |
| 76- Telecommunications and sound- recording equipment | 5.3 | 59 - Chemical materials and products, n.e.s. | -3.8 |
| 72 - Machinery specialized for particular industries | 5.3 | 58 - Plastics in non-primary forms | -3.5 |
| 32 - Coal, coke and briquettes | 4.9 | 53 - Dyeing, tanning and colouring materials | -2.2 |
| 81 - Prefabricated buildings; sanitary, etc., fixtures, n.e.s. | 3.3 | 01 - Meat and meat preparations | -2.0 |
| 77 - Electrical machinery, apparatus and appliances | 3.0 | 84 - Articles of apparel and clothing accessories | -1.8 |
| 79- Other transport equipment | 2.9 | 87 - Professional, scientific and controlling instruments, n.e.s. | -1.8 |
| 71 - Power-generating machinery and equipment | 2.8 | 55 - Footwear | -1.8 |
| 35 - Electric current | 2.1 | 52- Inorganic chemicals | -1.7 |
| Above divisions of SITC, Rev. 4, total | 130.2 | Above divisions of SITC, Rev. 4, total | -101.7 |
| Sections of SITC, Rev. 4 | Sections of SITC, Rev. 4 | ||
| 0+1+4 | Agricultural and food crude materials and products | 6 | Manufactured goods classified chiefly by material |
| 2+3 | Crude materials, inedible, and mineral fuels | 7 | Machinery and transport equipment |
| 5 | Chemicals and related products | 8+9 | Miscellaneous manufactured articles, commodities and transactions not classified elsewhere in the SITC |
1 All data are at current prices. Data for January–December 2007 have been updated and refer to 28 February 2008 closing date. Data for January 2008 are preliminary referring to 28 February 2008, data for February are preliminary referring to 31 March 2008 and data for March are preliminary referring to 28 April 2008.
2 In January–March 2008, in comparison to January–March 2007, CZK strengthened by 9.7% against EUR and by 25.3% against USD, both on average.
3 The Commonwealth of Independent States.
4 China, North Korea, Cuba, Laos, Mongolia and Vietnam.
5 Items CZ-CPA15 to CZ-CPA36
6 Import and export price indices in the Czech Republic are published later than data on the external trade of the CR.
7 See CZSO World Price Indices of Industrial Raw Materials and Food for March 2008.