Development of external trade price indices - 4. quarter of 2008 and year 2008
Product Code: e-7232-08
Quarter-on-quarter comparison:
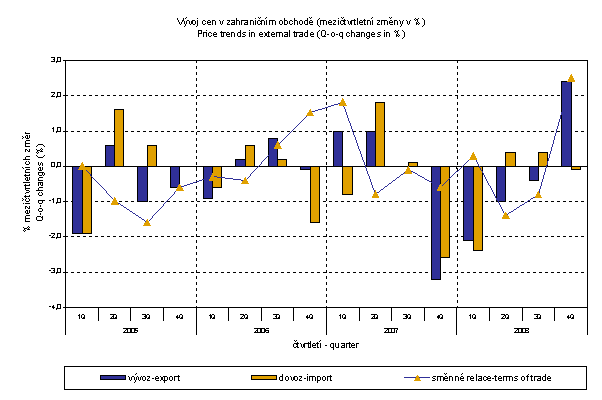
Export prices Q4 2008 compared to Q3 2008 increased by 2.4% (-0.4% in Q3). Import prices decreased by 0.1 % (+0.4% in Q3).
In export prices among more important groups prices grew most in 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' by 4.3%, 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by materials' by 4.2% and in 'machinery and transport equipment' by 3.9%. In contrast, prices dropped in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (-17.3%, mostly metal scrap), 'food beverages and tobacco' (-3.6%) and in 'chemicals and chemical products' (-0.8%).
In import prices only prices in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' dropped by 19.9% (especially petroleum and petroleum products). The most marked growth was recorded in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' by 8.0% (especially metaliferrous ores), 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' by 5.1% and prices in more important group 'machinery and transport equipment' increased by 5.0%.
External trade price development was again widely affected by the CZK exchange rate to the leading
foreign currencies.
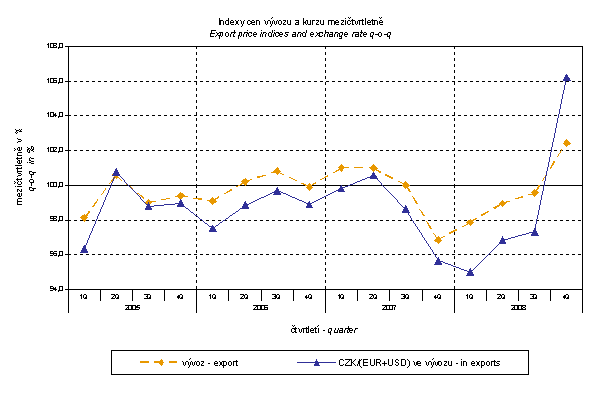
The q-o-q exchange rate index includes two most important currencies from the aspect of the Czech external trade, i.e. EUR and USD; q-o-q indices of CZK exchange rates to these currencies were weighted by the weight which pertains to those currencies in the export price index.
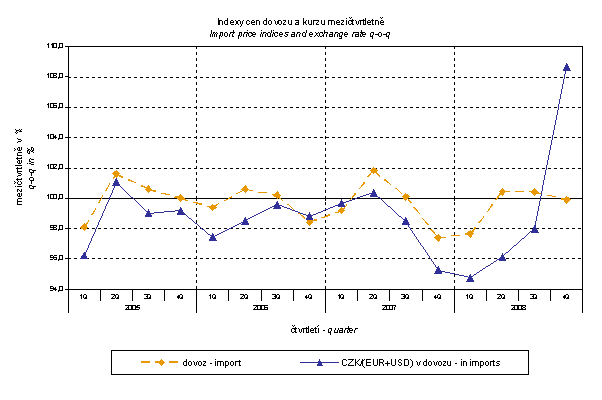
Similarly, when comparing with q-o-q import price indices, q-o-q EUR and USD exchange rate indices were weighted by the weight which pertains to these currencies in the import price index.
Thus, it becomes clear that in both the imports and exports, external trade prices have a strong relation to exchange rate impacts. This relation could naturally be even stronger in m-o-m comparison, however, also in q-o-q index it is relatively strong as shown in graphs. It is rather logical conclusion because the contracts with foreign entities are, as a rule, signed for a longer period of time and the longer is the contract period, the stronger is the relation to exchange rates.
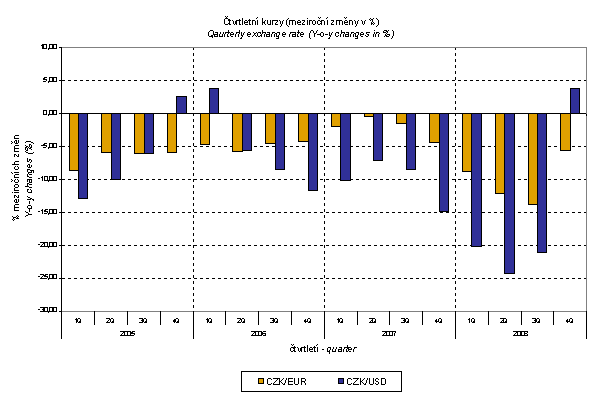
The above graphs clearly show that lower growth rate of strengthening of the CZK to EUR and a modest weakening to USD in Q3 2008 resulted to a moderate drop of export price indices and even a slight growth of the import price index. In Q4 CZK weakened significantly and especially to USD which showed even in export price growth. Import prices did not follow this trend which can be attributed to oil price drop.
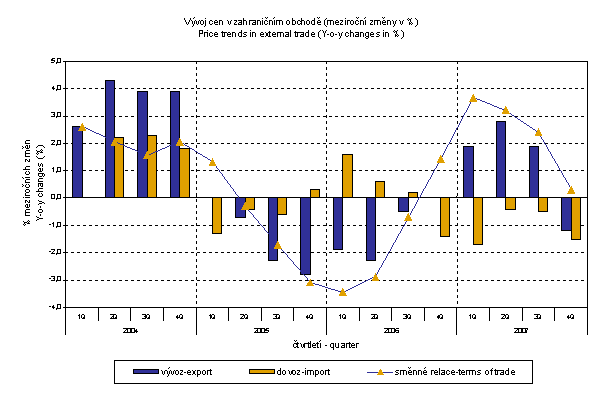
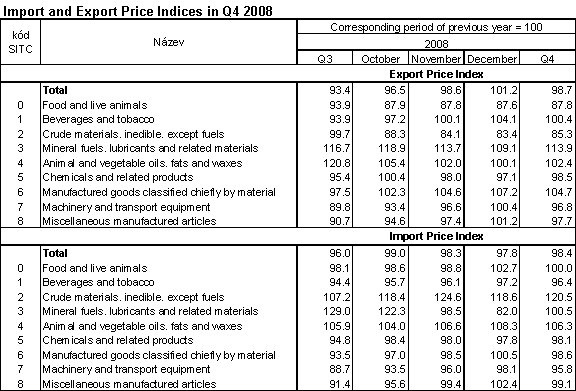
In Q4 2008, the value of terms of trade compared with Q3 2008 was 102.5% (in Q3 99.2%). In groups important in terms of weight positive values of terms of trade were recorded in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (121.3%), 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by materials' (103.6%). In contrast, negative values were recorded in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (76.6%), 'food, beverages and tobacco' (94.2%) and 'machinery and transport equipment' (99.0%).
Year-on-year comparison:
In Q4 2008 export prices fell by 1.3 % (-6.6% in Q3). Prices continue to fall from Q4 2007. More profound drop came especially from the strengthening of CZK to EUR and USD. The most significant price drops were recorded in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (-14.7%), 'food, beverages and tobacco' (-12.2%) and 'machinery and transport equipment' (-3.2%, especially road vehicles). Among more important groups price growth was reported only for 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (+13.9%, especially coal) and 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' (+4.7%).
Import prices decreased in Q4 2008 by 1.6 % (-4.0 % in Q3 2007). The price drop was attributed to a strong CZK exchange rate. The most marked price decline was recorded in 'machinery and transport equipment' (-4.2%, especially road vehicles), 'chemicals and chemical products' (-1.9%) and 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' (-1.4%). Among more important groups growing were only prices in 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' (+20.5%) and prices in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (+0.5%, especially gas).
Terms of trade reached in Q4 2007 the value of 100.3 %, y-o-y, (i.e. by 3.0 p.p. more than in Q3 2007) and after three quarters they turned into positive values – see graph below. The highest value was recorded for 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (113.3%) and 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' (106.2%). 'Machinery and transport equipment' reached 101.0%. Among more important groups the terms of trade negative values were recorded in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (70.8%), 'food, beverages and tobacco' (87.8%) and 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' (98.6%).
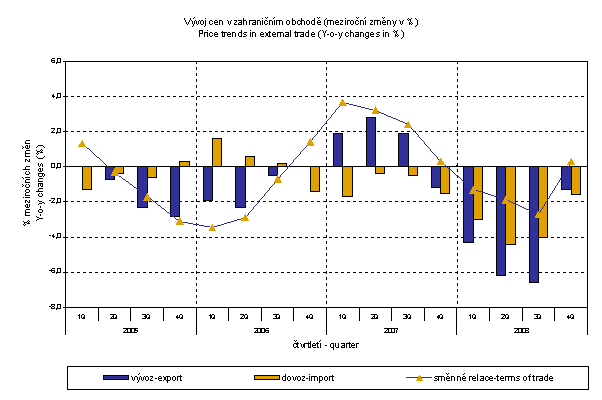
Different development trends in export and import prices in this quarter were harmonised since Q4 2007.
As it was shown above, external trade prices are exposed to many effects, among other things, also to the CZK exchange rate to foreign currencies. This influence is important and often even decisive mainly in m-o-m expression; however, it is very significant in the quarter-on-quarter comparison and markedly affects also the level of y-o-y external trade price indices. CZK exchange rate to EUR moderately strengthened, y-o-y, while to USD it slightly weakened which corresponds to lower growth rate of external trade price indices. The development of quarterly exchange rates (y-o-y changes) is clear from the graph below.
Development of external trade price indices in 2008
Year-on-year comparison:
- -On average, over the whole year 2008 export prices dropped by 4.6% (+1.3% in 2007), import prices decreased by 3.3% (-1.0 % in 2007). The external price development in 2008 was affected by CZK strengthening to EUR and USD, which pushed these indices down while the price growth in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' pushed them up.
- In export more marked price drop was recorded in 'machinery and transport equipment' (-7.2%, especially road vehicles), 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' (-6.6%) and in 'chemicals and chemical products' (-4.8%). Among more important groups higher were only prices in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (-15.6%, especially coal).
- In import the most biggest drop was recorded in 'machinery and transport equipment' (-8.2%, mainly electrical machinery and apparatus), 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' (-6.2%), prices in 'chemicals and chemical products' and 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' decreased both by 4.6%. In contrast, among more important groups the most biggest price growth was reported for 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' by 17.3% (especially petroleum and petroleum products) and in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' by 8.2%.
- Terms of trade reached in total negative value of 98.7% in 2008 (102.3% in 2007). However, the terms of trade figures started to grow in Q4 2008 to reach 100.3%.
Export price indices adjusted y-o-y by exchange rate
The CZSO makes experimental calculations of monthly external trade price indices adjusted for exchange rate influence. The method used does not allow due to many practical reasons to make a 100% exchange rate adjustment (i.e. not all observed deals made in foreign currencies are for the needs of calculations of external trade price indices also reported as such – this share, however, makes only about 30 %). Nevertheless, it was verified that despite the increasing share of reporting in foreign currencies the currency basket remains basically constant. Thus, it can be stated that at the full exchange rate adjustment the differences between the published price indices and price indices that were adjusted would be even bigger.
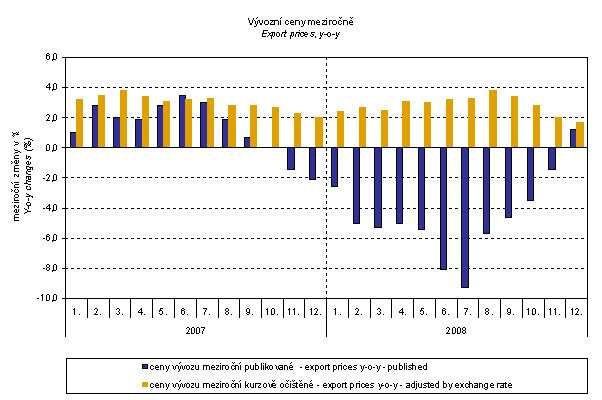
It is clear from the graph that the exchange rate was important also for export price indices. For the whole observed period except for June 2007, it decreased their amount (CZK was mostly strengthening to foreign currencies). In June, the exchange rate increased the price index due to weakening of CZK to EUR. After elimination of the exchange rate influence, export prices would have been increasing in all months in 2007 and 2008: In 2008, especially in July it is obvious how a strong exchange rate affected the external prices decrease.
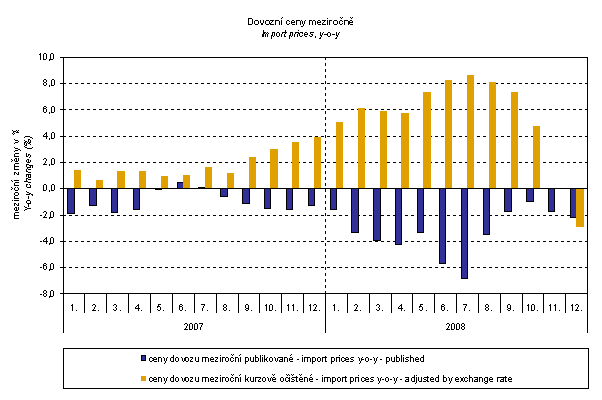
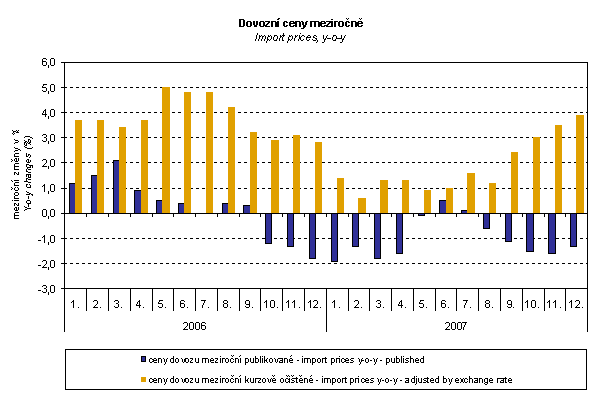
The graph above shows that the exchange rate markedly influenced also the import price indices. For the whole observed period except of December 2008 it decreased their amount. After elimination of the exchange rate influence, export prices would have been increasing from January 2007 until November 2008. Like in exports, there is a strong exchange rate influence in June and July 2008 resulting into a marked drop of import prices. Conversely, in December 2008 the exchange rate influence increased the import price index which came from weakening of CZK to USD. CZK moderately strengthened to EUR.
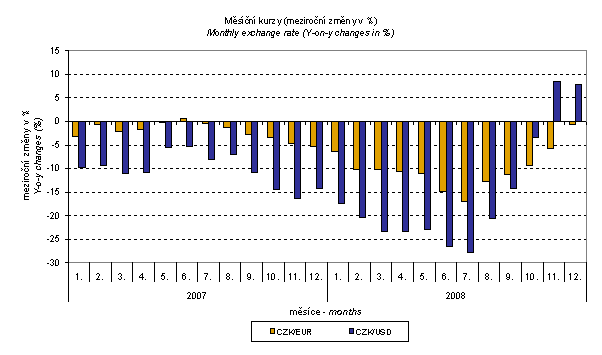
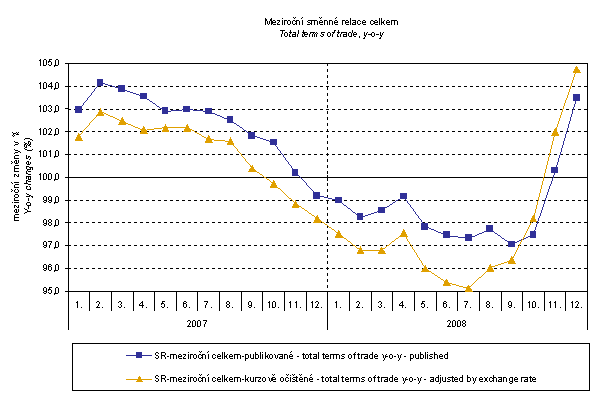
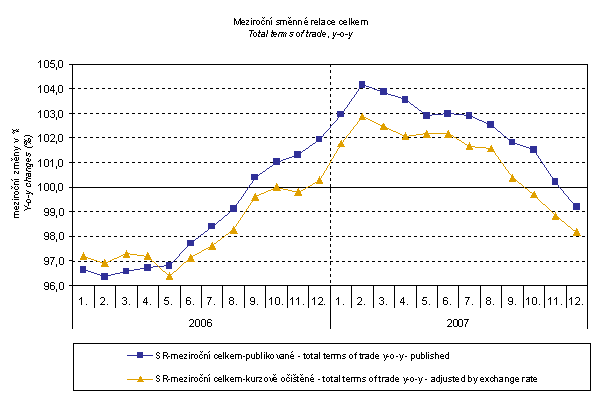
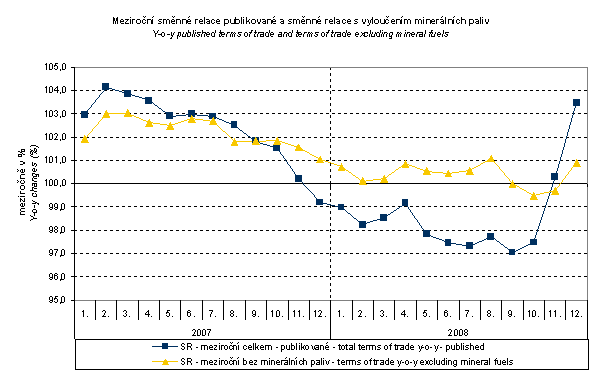
From the above graph it is clear that in the period from January 2007 to September 2008 the exchange rate pushed the y-o-y terms of trade values up and from October 2008 it pushed them down. This happened due to the fact that in the currency basket there is higher proportion of USD in imports compared to exports. As it is obvious from the graph Monthly Exchange Rates in November and December 2008 CZK strengthened to EUR and, concurrently, weakened to USD. From February 2007, with a little exception in June 2007, the terms of trade values were decreasing continually until December 2007 when, for the first time after sixteen months, they showed negative values. In March and April 2008 the terms of trade increased, however, from May they began to fall, even more profoundly, to negative values. In August 2008 the terms of trade figure moderately increased but in September due to the exchange rate influence, they fell again. From October 2008 the terms of trade resumed their growth.
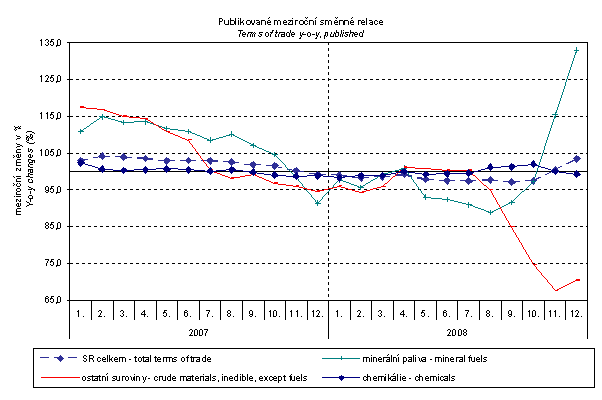
What other reasons caused a gradual drop of the y-o-y terms of trade? The above graph includes groups showing more significant downward trend in the terms of trade development since 2007. This applies to 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (especially metaliferrous ores and metal scrap) where import prices grew faster than export prices and where import prices have been falling since September 2008. An interesting group is, however, especially the group fuels and related chemicals (especially plastics). The growth of exchange rate adjusted terms of trade in the previous graph from August to December 2008 can be attributed to the increase of terms of trade mainly in fuels and related chemicals. How would the terms of trade value develop if the observed groups would not include 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials'?
As it is clear from the above graph, 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' increased the total value of the y-o-y terms of trade in the period from January to September 2007, and in the period from October 2007 to October 2008 they pushed the terms of trade value down and in November and December 2008 mineral fuels again had a upward effect on the terms of trade value. It is naturally related to the world market price development, especially to crude oil prices. Import prices which compared to export prices include higher proportion of crude materials respond more sensitively to price turbulences and therefore when prices of crude materials go up, terms of trade, as a rule, go down and, conversely, when prices of crude materials fall, terms of trade grow.
The following table shows published external price indices without adjustment
Prapared by: Vladimír Klimeš, price statistics department
Branch director: RNDr. Jiří Mrázek, tel. 274 052 533
