Development of external trade price indices - 3. quarter of 2007
Product Code: e-7232-07
14 November 2007
Development of external trade price indices in the third quarter of 2007
Quarter-on-quarter comparison:
Export prices showed no changes in Q3 2007 compared to Q2 2007 (in the last quarter they grew by 1.0%). Import prices increased by only 0.1 % in Q2 by 1.8%).
In export prices the most marked increase (+5.2%) was recorded in 'food, beverages and tobacco' (especially 'cereals and cereal preparations'). In most of observed groups prices slightly dropped, among groups most important in terms of weight a moderate price drop was reported in 'manufactured good classified chiefly by material' by 0.5% (mainly non-ferrous metals) and in 'machinery and transport equipment' by 0.2% (namely 'power generating machinery and equipment').
In import prices the most marked growth (+4.6%) was observed in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' (metaliferrous ores in particular), from groups important in terms of weight an increase was recorded also for prices of 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' (+2.0%). Conversely, the most significant drop was recorded for prices of 'chemicals and related products' by 1.2% (inorganic chemicals in particular). Prices of 'machinery and transport equipment' dropped by 0.4% (especially metal working machinery).
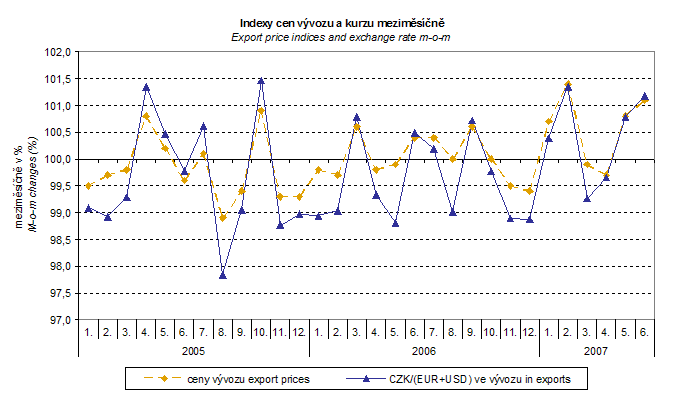
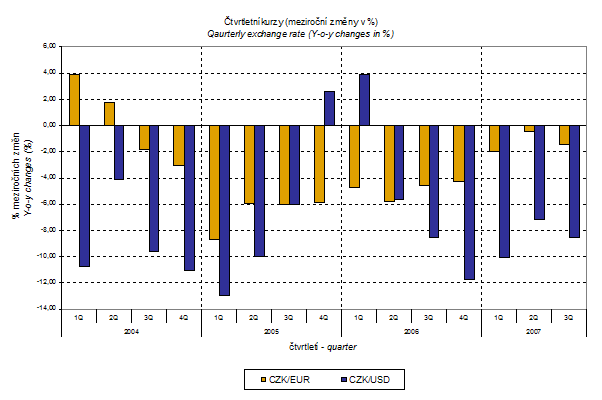
External trade price development was again widely affected by the CZK exchange rates to the leading foreign currencies.
The q-o-q exchange rate index includes two most important currencies from the aspect of Czech external trade, i.e. EUR and USD; q-o-q indices of CZK exchange rates to these currencies were weighted by the weight which pertains to those currencies in the export price index.
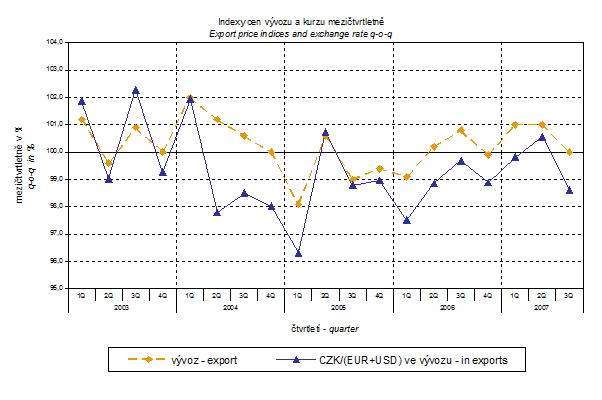
Similarly, when comparing with the q-o-q import price indices, q-o-q EUR and USD exchange rate indices were weighted by the weight which pertains to these currencies in the import price index.
Thus, it becomes clear that in both the import and export, the external trade prices have a strong relation to exchange rate impacts. This relation could naturally be even stronger in m-o-m comparison, however, also in q-o-q index it is relatively strong as shown in graphs. It is rather logical conclusion because the contracts with foreign entities are, as a rule, signed for a longer period of time and the longer is the contract period, the stronger is the relation to exchange rates.
In Q3 2007, the value of terms of trade compared with Q2 2007 was 99.9 % (in Q2 2007 it was 99.2 %). In groups important in terms of weight negative values of terms of trade (94.4%) were recorded in 'crude material, inedible, except fuels' (especially metaliferrous ores), in 'manufactured goods classified chiefly by material' 99.6% (especially products of wood and cork) and in 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' 99.7% (footwear, in particular). Conversely, positive values of terms of trade were recorded in 'machinery and transport equipment' 100.2% (mainly office machinery and automatic data-processing machines), in 'chemicals and related products' 100.9% and 'food, beverages and tobacco' 104.3 %.
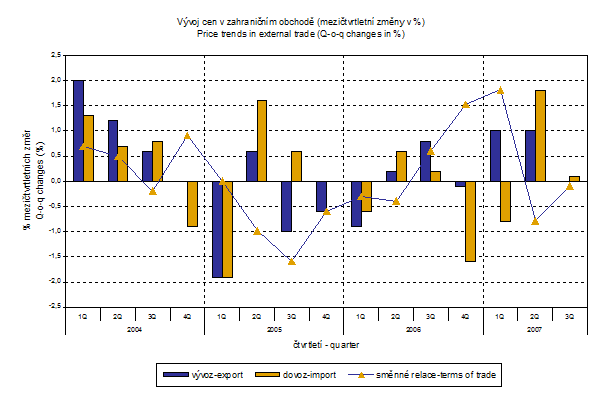
Year-on-year comparison:
In Q3 2007 export prices rose by 1.9 % (in Q2 by 2.8%). The prices reduced their growth due to strengthening of CZK to EUR and USD. The most significant growth was recorded for prices of 'food, beverages and tobacco' by 14.8 % (mainly 'cereals and cereal preparations') and in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' by 11.3% (mainly 'oil-seeds and oleaginous fruits'). Prices in 'machinery and transport equipment' remained unchanged. A drop was recorded only for one group, i.e. 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' by 0.4%.
Import prices decreased in Q3 2007 by 0.5 % (in Q2 2007 by 0.4 %). The price drop was attributed to a strong CZK exchange rate. The group most important in terms of weight 'machinery and transport equipment' showed the most marked drop by 2.9 % (mainly office machines and automatic data-processing machines) and continues to fall for the fourth quarter in a row. Prices decreased also in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' by 2.6% (especially natural gas) and in 'miscellaneous manufactured articles' by 1.9%. Prices in all other groups grew. Among groups important in terms of weight increasing prices were recorded mainly in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' by 12.2% (metaliferrous ores, in particular).
Terms of trade reached in Q3 2007 y-o-y positive value of 102.4 % (i.e. by 0.8 p.p. less than in Q2 2007). Y-o-y terms of trade were showing positive figures continuously since Q4 2006 – see graph below). The highest values were in 'food, beverages and tobacco' 110.1 %, in 'mineral fuels, lubricants and related materials' 108.6% and in 'machinery and transport equipment' 103.0 %. Among groups important in terms of weight negative values were recorded only in 'crude materials, inedible, except fuels' 99.2%.
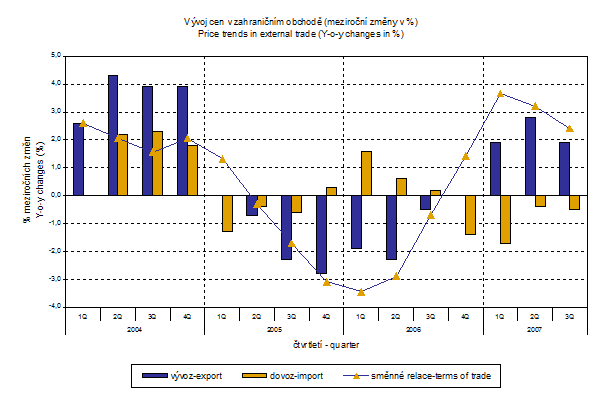
What was the reason for the different price development of import and export prices? As it was shown above, external trade prices are exposed to many effects, among other things, also to the CZK exchange rate to foreign currencies. This influence is important and often even decisive mainly in m-o-m expression; however, it markedly affects also the level of quarter-on-quarter external trade price indices. The development of y-o-y changes of exchange rates is clear from the graph below.
Year-on-year external trade price indices adjusted by exchange rate
The CZSO makes experimental calculations of monthly external trade price indices adjusted for exchange rate influence. The method used does not allow due to many practical reasons to make a 100% exchange rate adjustment (i.e. not all observed deals made in foreign currencies are for the needs of calculations of external trade price indices also reported as such – this share, however, makes only about 30 %). Nevertheless, it was verified that despite the increasing share of reporting in foreign currencies the currency basket remains basically constant. Thus, it can be stated that at the full exchange rate adjustment the differences between the published price indices and price indices that were adjusted would be even bigger.
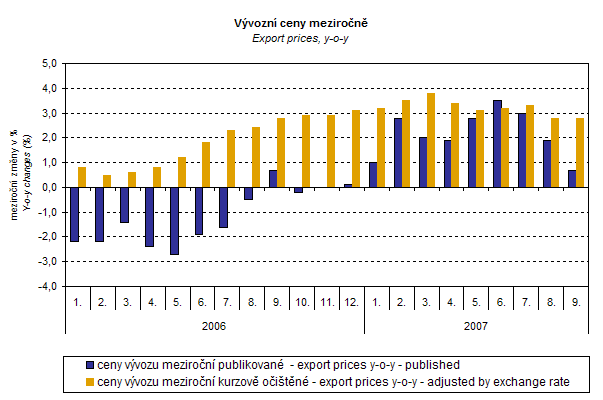
It is clear from the graph that the exchange rate was important also for export price indices. For the whole observed period except for June it decreased their amount (CZK was mostly strengthening to foreign currencies). In June the exchange rate increased the index due to weakening of CZK to EUR. After elimination of the exchange rate influence, export prices would have been increasing in all months.
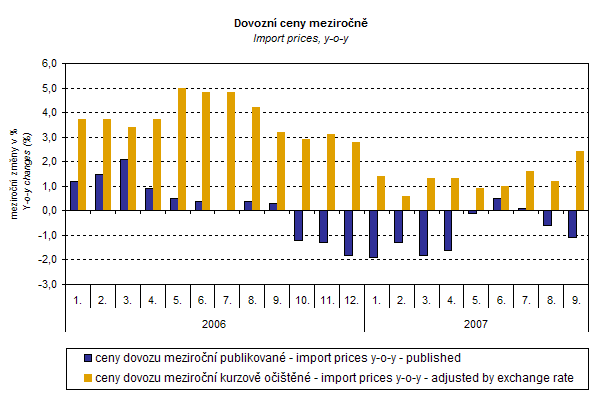
The graph above shows that the exchange rate markedly influenced also the import price indices. For the whole observed period it decreased their amount. After elimination of the exchange rate influence, export prices would have been increasing in all months.
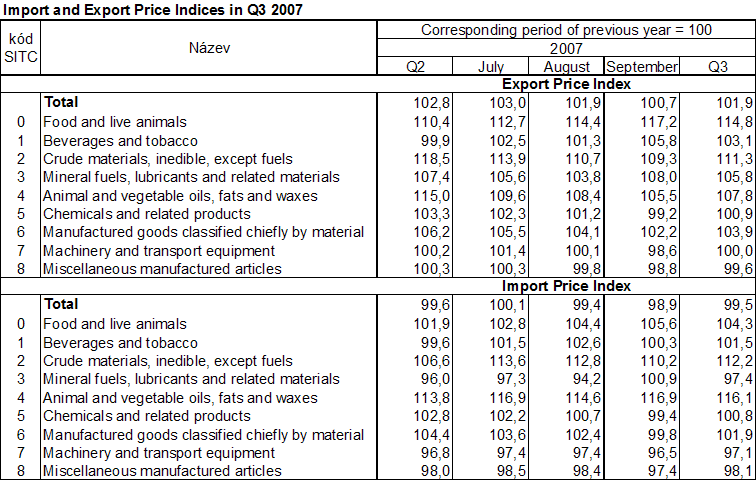
The following table shows published external trade price indices without adjustment.
Zpracoval: Ing. Vladimír Klimeš, odbor statistiky cen
Ředitel odboru: RNDr. Jiří Mrázek, tel. 274 052 533
