Indicators of Social and Economic Development of the Czech Republic
Methodological Notes | Contents |
This publication presents annual time series (mostly from the year 1985), quarterly time series and (exceptionally) monthly time series. Shown in addition to absolute figures are indices, too. Unless stated otherwise in the tables or methodological notes, the index describes the state in the reference period related to the state in the corresponding period of the preceding year, all governed by the same prices, methodology and organisational structure.
Population
Figures showing the population size, structure and their changes are derived from decennial population censuses and additional information on population balances and vital statistics linked to the censuses.
The figures on the population and vital statistics cover Czech residents, irrespective of citizenship. The data for 2001 and later years are derived from the Population and Housing Census 2001 and also include foreigners with 90+ day visas staying in the CR more than one year (as stipulated by Act No. 326/1999 Sb., on the Stay of Foreigners) and foreigners who were granted asylum (pursuant to Asylum Act No. 325/1999 Sb.). Since 1 May 2004, following up the so-called Euro-amendment to Act No. 326/1999 Sb., on the Stay of Foreigners, the data have been referring to citizens of the EU member states with temporary stay in the Czech Republic and citizens of third countries with long-term stay.
The presented data also include marriages, births and deaths of Czech citizens with permanent residence in the CR, which occurred abroad.
Relative rates are defined per 1 000 individuals (mid-year population), infant mortality is shown in terms of the number of deaths up to 1 year of age per 1 000 live births.
Gross domestic product
The gross domestic product of the Czech Republic – the key indicator of the system of national accounts – and the principal components of GDP expenditure are calculated in compliance with the principles of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 95).
Gross domestic product is the sum of values added by all industries of activities considered productive in the system of national accounts (i.e., including market and non-market services). Its calculation uses purchase prices, at which market outputs are implemented (i.e. including taxes on products and excluding subsidies on products). For non-market services, output is the sum of intermediate consumption, compensation of employees and fixed capital consumption. Initial calculations are made at current prices and the results are deflated to constant prices so that development not affected by price fluctuations can be monitored.
Final household consumption expenditure comprises the value of goods and services used by households to satisfy their individual needs, paid for from household incomes of and acquired by purchase, as gifts or consumption in kind. Purchases for business activities are excluded.
Final consumption expenditure by government and private non-profit institutions serving households (including membership organisations) is the value of non-market services provided by the above-mentioned institutions to satisfy individual and collective needs. It is paid from the state budget, local government budgets and other contributions. The final consumption expenditure is quantified as the difference between outputs as described above and incomes from own activities (e.g. taxes, penalties, and fees are not counted in) of all budgetary and most semi-budgetary organisations providing non-market services, as well as of health insurance companies and non-profit private institutions serving households. The common characteristic of these institutions is that their activities are not motivated by the making of profits.
Gross fixed capital formation includes the value of acquired tangible and intangible fixed assets purchased, taken over or produced on own account mines disposals of these assets. Acquisition via financial leasing is included, too. An objective of the acquisition is always to use these fixed assets for productive activities. The indicator excludes consumer durables acquired by households to satisfy final consumption.
Gross capital formation through changes in inventories, reserves and valuables is calculated as the difference between additions to and drawings on the inventories.
Exports minus imports (net exports) describe the resulting impact of external trade in goods and services on the possibility to use the production by residents. These figures are derived from the outputs of statistical survey on export and import of goods in relation to the EU Member States (in Intrastat system) and from wide monitoring in relation to other countries (customs declaration). Data on income from and expenditure on services are obtained from statistical survey and the balance of payments.
State budget current performance
Given are only total incomes, total expenditures and state budget surplus/deficit, governed by the methodology and prices in force in the individual years. The figures exclude the federal budget that had existed by 1992. Shown are state budget revenue and expenditure related to the end of period. The annual figures include the final state budget valid for given year.
Deposits and credits of households, total
Deposits of households in and credits of households from resident financial institutions include data (in domestic and foreign currencies) for the sector of households (i.e. for individual citizens and small unincorporated entrepreneurs). The source underlying the presented information is data provided by the Czech National Bank.
Producer price indices
Price indices calculated according to new revised index patterns based on the structure of 2005 have been released since 2007.
Index patterns, selection of price representatives and reporting units (respondents) were revised in the framework of a comprehensive revision, which took place for individual price groups in 2006. The weights are based on sales (yields) reached in 2005.
At the same time the base price period was changed; it is the average of 2005 for the new price indices published since 2007.
The indices are derived from prices of the samples of representatives and selected reporting units by aggregating simple price indices of the representatives into totals using the Laspeyres formula in a modified form. Constant weights of 2005 are used for calculation.
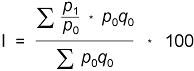
where
p1 is the price in the reference period,
p0 is the price in the base period,
poqo is the constant weight - the value indicator of the base period (sales, yields in 1999).
The continuation of the time series published up to the end of 2006 was done as follows:
For industrial producers or construction works this continuation of already published price series by the end of 2006 which remain valid and revised indices published since 2007 is ensured by means of coefficients (conversion bridges) calculated from the ratio between the revised and original indices for December 2005 over December 2004, i.e. Q4 2005 and Q4 2004.
For other price ranges the original time series of indices for 2005 and 2006 were replaced by new calculated indices with base price period, i.e. the 2005 average. Price development for 2004 and preceding period was retrapolated by time series of the original system.
Agricultural producer price index
The price index of agricultural producers is derived every month from prices collected among approximately 650 selected producers in agriculture (private, cooperative and state-owned companies) and does not include VAT. Collected are contract prices (excluding own consumption) designed for the domestic market and direct exports to abroad.
Since 2007 prices of 95 basic agricultural products (price representatives) are collected, of which 63 are plant products (including fruit and vegetables) and 32 animal products.
Average prices of measured products are calculated as a simple arithmetic mean of prices of individual producers.
A constant weight pattern is used to calculate individual, group and aggregate price indices. This weight pattern is based on the structure of sales of agricultural products output in the months of 2005, which are the base price period.
Forestry (raw timber) price index
Forestry (raw timber) price index is measured from 2007 on quarterly basis, using prices collected among over 120 selected raw timber producers and excluding VAT. Measured are realisation and contract prices (excluding own consumption) designed for the domestic market.
Prices of 18 basic ranges of hardwood and 19 of softwood products (price representatives) have been measured in forestry.
Average prices of measured products are calculated as a simple arithmetic mean of prices of individual timber producers.
A constant weight pattern is used to calculate individual, group and aggregate forestry price indices. This weight pattern is based on the structure of sales of timber output in 2005.
Industrial producer price index
New revised index patterns have been used to calculate industrial producer price indices since January 2007. These index patterns are based on the structure of domestic sales in 2005 (former indices from the structure of domestic sales in 1999).
The new revised index pattern of industrial producer prices valid since 2007 contains the total of 4 713 price representatives measured among 1 200 reporting units (previously 5 760 representatives and 1 352 respondents).
The index is calculated on monthly basis, using prices collected on state statistical questionnaire Ceny Prům1-12. Reported prices are those contracted between the supplier and the customer for products designed for the Czech market, excluding VAT, excise tax and the costs of transport to the customer and related costs. The period for price collecting was extended and includes prices between 1st and 18th calendar day of the reference period (originally between 10th and 12th calendar day).
Constant weights are based on the structure of domestic sales for 2005 taken from questionnaire P 5-01 (for CZ-CPA 4-digit classes), questionnaire Prům P 2-01 (for CZ-CPA 6-digit subcategories and individual respondents), further, from questionnaire Ceny Prům 1-12 (for CZ-CPA 6-digit subcategory and individual representatives).
Price indices of construction work, types of constructions and construction output costs
Following up the revision of price indices, a new, advanced type of statistical reporting (so-called “shuttle”) was put into use in 1995 to determine construction work price index: the questionnaires are not changed for at least 2 years and are returned from the reporting unit to the state statistical service and back. The questionnaire for the years 2007 - 2008 contains 144 chosen price representatives (selected types of construction work) plus a form to be used to propose a new representative, for which a given reporting unit gives details of implementation conditions according to its needs.
Prices are reported quarterly and they are prices negotiated between the supplier and the customer for a unit of construction work, including material, for domestic construction. Division 45 of the Standard classification of production (CZ-CPA) was employed to classify prices of construction work, while the CZ-CC was used to classify types of constructions. As a rule, prices of construction work are always measured for the second month of a given quarter and do not include VAT.
After 2006 revision, 2005 construction output volume is taken for the constant weight basis of the index and the 2005 average is the base period. Since 2004, indices of construction work costs and indices of prices of construction output material inputs have been measured. They were derived retroactively back to 2001. The reporting network was established by purposive sampling of respondents from all the size categories (up to and over 19 employees) and various legal forms.
The quarterly survey and calculation of price indices of construction work and of types of constructions are supplemented by monthly estimates of trends in construction work prices. Estimates of monthly price development are always detailed retroactively upon a quarter (45th day) in compliance with the results of direct quarterly price collection. December 1999 was taken the base period for estimates of construction work price development
Price index of market services
The aggregate price index of market services published for the first time in January 1997 has been available in a monthly time series since December 1993. It includes the following price indices of market services in business sphere (i.e. enterprises): price indices of goods transport and storage; post and telecommunications; financial intermediation except insurance and pension funding; insurance and pension funding; business services; real estate, renting services and sewage rate.
Price surveys of the above-mentioned market services, which are aggregated into the aggregate price index, comprise selected services included under the following Divisions of the CPA: 60, 61, 62, 64, 65, 66, 70, 71, 72, 74, and 90.
The methodology of surveying the individual services is described with the price indices of services published separately.
The constant weight of the aggregate index is the sum of the weights for individual services in 2005.
Goods transport and storage price index
Since 1 January 1995 the goods transport and storage price index has been derived from data collected among selected reporting units. Prices are surveyed excluding VAT, on constant price representatives and their constant transport distances. They are contract realization prices designed for the domestic market. The aggregate goods transport and storage index includes indices for transport by rail, road, pipeline, inland water and air transport and cargo handling and storage, which are calculated separately.
Constant weights are revenues from transport charges or storage in 2005. The 2005 average is taken for the base period.
Price index of posts and telecommunications
The price index of posts and telecommunications has been calculated monthly since 1993 from prices collected among selected reporting units. The prices are measured on a total of 44 chosen representatives.
The prices of posts and telecommunications are collected exclusive of VAT. Surveyed are both contract prices (excluding own consumption) and those fixed by government under its central price regulation. They are mostly prices of services (outputs) designed for the domestic market.
Posts and telecommunications include postal activities (delivery, finance and mediation), telecommunications and radio communications. The weight pattern is based on 2005 communications yields. The base period is the 2005 average.
Price index of financial intermediation, except insurance and pension funding
This price index has been calculated monthly since December 1993 from data collected among selected reporting units of financial intermediation classified to the banking sector according to CZ-CPA, code 65.12, using questionnaire Ceny Ban 2-12. Questionnaire Ceny Leas 1-12 is used to collect data among selected reporting units of other financial intermediation providing financial leasing, classified under CZ-CPA, code 65.21.
The financial intermediation survey is focused on prices of selected banking services provided by commercial banks to enterprises. Financial leasing service prices are measured among four major leasing companies for chosen areas of leasing provided to business sphere. The price of leasing is a leasing coefficient, which is calculated always from prices excluding VAT.
Constant weights of the index are revenues from financial activities of commercial banks and lease increases for financial lease services related to the base year of the comprehensive revision of price indices. The base period is the 2005 average.
Insurance price index
Insurance price index has been calculated monthly since 1995 on the basis of data collected among selected reporting units (5 largest insurance companies operating on the domestic market). Surveying is directed to the insurance of the business sphere only.
The price is always the premium for a given representative, which is calculated from the rates of insurance companies (in per cent or per mille) and the sum insured of property under insurance. Hence, price movement outside the domain of insurance considerably influences the growth of insurance prices.
The aggregate index of this entrepreneurial, so-called other insurance, as laid down in the national Standard Classification of Production (CZ-CPA) – Class 66.03, contains indices of property fire insurance and insurance against theft (broken down into crafts, trade and services), insurance of motor vehicles (passenger cars and trucks), and insurance of agricultural production (plant and animal products).
A constant weight pattern determined from premiums received for 2005 has been established to calculate individual and group price indices, as well as the aggregate index. The base period is the 2005 average.
Real estate, renting and business activities price index
This price index has been calculated since 1994. Surveyed are chosen respondents providing market services predominantly for entrepreneurs.
The survey covers prices of services classified in the national Standard Classification of Production (CZ-CPA) in divisions 70 - Real estate activities, 71 - Renting of machinery and equipment without operator, 72 - Computer and related activities, and 74 - Other business activities (namely legal and tax consultancy, accounting, book-keeping and auditing activities; architectural and engineering activities; advertising; investigation and security activities, industrial cleaning; translation activities; fair and exhibition activities).
A constant weight pattern determined on the structure of sales of services provided in 2005 has been established to calculate individual and group price indices, as well as the aggregate index. The base period is the 2005 average.
Sewage rate indices (sewage water)
The sewage rate index is calculated of sewage water prices surveyed on monthly basis. The prices are contract, realization ones excluding VAT and designed for the domestic market. Average prices are calculated as weighted arithmetic mean of prices reported by 44 water management organisations. Constant weights are determined on the basis of sales structure for 2005 on monthly basis. The base period of index is the average for 2005.
The price index of water supply (drinking water) is part of industrial producer price index; therefore, it is not indicated separately.
Consumer prices
Trends in consumer prices are measured on consumer baskets based on a sample of goods and services paid for by the population. Price representatives include such products and services, which account for an important share in population’s expenditure and cover the entire sphere of consumption. Their total number is about 730.
Weights for the consumer baskets, which have been used to calculate consumer price indices since 2007, are based on household expenditure data according to family budget statistics for 2005 corrected by national accounts statistics.
The prices of individual kinds of goods and services are collected on a monthly basis among selected shops by the staff of the CZSO.
Consumer price indices are derived from the Laspeyres formula and the weights are constant. The base period is December 2005.
Money income and expenditure of households
Data on household income and expenditure are taken from the sample survey of household budget statistics. The sample unit and reporting unit is a household, i.e. people sharing a dwelling and running a common budget. Purposive quota sampling is used for household budget statistics.
Before and in the year 2005, basic sampling attributes were social group of a household (it was determined according to which social group the head of household belonged to) and net money income per person. The third sampling attribute was the number of unprovided-for children (in households of economically active persons) or the number and sex of members (in households of pensioners without active members).
From 2006, the sampling attribute is economic activity and position of a person in the head of household. Households of economically active persons are classified by status in employment or education of the person in the head. Households with an economically inactive person in the head are further broken down depending on whether someone of the other members of the household is economically active.
For three the most important groups of households some more sampling attributes are used:
- Net money income per household member and number of unprovided-for children for households of employees and households of self-employed persons.
- Income per household member and number of members or their sex for households of pensioners without economically active members.
Data published (monthly averages in CZK per person):
1. Average household (before and in the year 2005) or households in total (since 2006); before 2005, some less frequent types of households were not present in the sample (e.g. households of the unemployed, of pensioners with economically active members, etc.) An estimate of the average household of the sample was produced by re-weighting according to social groups (based on the households structure from Microcensus), which eliminated the disproportion between individual social groups in the sample. From 2006, the sample includes all types of households represented in the population; number of pensioners without economically active members is reduced. During the processing, the disproportion is eliminated by re-weighting; thus, the share of individual groups of households corresponds to their real distribution in the population.
2. Households of employees; households of persons in employment or service relationship, who work either based on a contract of employment or an agreement to perform work or an agreement to complete a job. Employees are also working members of producers´ cooperatives (including agricultural), partners of private limited companies and limited partners of limited partnership companies, who work for a company based on a contract of employment and receive remuneration for it, which is revenue from employment.
3. Households of pensioners, economically active members excluded, are households of persons receiving any kind of pension (orphan’s pension excluded), who do not work at all or their work activities are only of limited scope (i.e. their annual income from work must not exceed CZK 12 000); this limit is valid also for the other members of a household.
Definitions of items:
Net money income and net money expenditure embrace all money income/expenditure minus health and social security insurance and advances on income tax. They exclude also savings withdrawn, received cashless loans, credits and loans or deposits, repaid cashless loans, credits and loans to private persons. Net money income is one of the selection criteria; the development of it is thus naturally determined in advance and therefore it has to be understood as additional information.
Individual expenditure groups include:
Food and non-alcoholic beverages - all kinds of food products and non-alcoholic beverages purchased for consumption at home;
Alcoholic beverages and tobacco - all kinds of alcoholic beverages (incl. cocktails and non-alcoholic beer) purchased for consumption at home, tobacco and products thereof;
Clothing and footwear - clothing materials, underwear, knitted garments, ready-to-wear garments, garments for sport and work, incl. made-to-measure garments, cleaning, repair and hire of clothing; footwear of all kinds, incl. made-to-measure footwear, repair of footwear, shoe cleaning;
Housing - rentals, water rate and sewage charges, refuse collection and other municipal services, heat, hot water, electricity and gas supply, solid and liquid fuels, products and services for the routine maintenance, repair, reconstruction and construction of the dwelling;
Furnishings, household equipment and routine maintenance of the house - furniture and furnishings, floor coverings, household textiles, bed linen, household appliances (refrigerators, washing-machines, cookers, vacuum cleaners, etc.), glassware, ceramic ware and chinaware, tools and equipment for house and garden, goods and services for routine household maintenance (cleaning and maintenance products, window cleaning, dry-cleaning and laundering of carpets, etc.);
Transport and communication - purchase of vehicles, operation of personal transport equipment (fuels and lubricants, spare parts and accessories, repair and maintenance, other services in respect of personal transport equipment, such as hire of garages or parking spaces not providing parking in connection with the dwelling, hire of cars, motorway tax disc, driving lessons, etc.), all kinds of public passenger transport and transport services, postal services, purchase of telephones, accessories and phone cards, phone services, incl. information transmission services;
Leisure - equipment for the reception, recording and reproduction of sound and pictures (television sets, video-cassette players and recorders, radio sets, tape players and recorders, cassette players and recorders, CD-players, still cameras, computers, incl. software) and repair thereof, recording media (records, video cassettes, compact discs, tapes and cassettes, films), other major durables for recreation and culture, musical instruments, games, toys and hobbies, gardens, plants and flowers, pets and related products, veterinary services, recreational, cultural and sporting services, charges for television and radio broadcasting, newspapers, books and stationery, package holidays;
Catering and accommodation services - meals (excl. drinks) at restaurants and other catering facilities, incl. on public transport, wedding and other feasts at catering facilities, supply of cooked dishes, catering services of work canteens, office canteens and canteens in schools, universities and other educational establishments, accommodation services of hotels, boarding houses, youth hostels, camping sites, etc;
The contents of the other items are given by their titles.
Starting with 1999, expenditure of households is classified according to CZ-COICOP (Classification of Individual Consumption by Purpose). Its implementation changed the way of classifying items; at the same time, the contents of some measured items changed significantly, compared with the classification used before 1999. For the purpose of data comparability in the time series, the contents of the groups had to be adjusted; therefore, they precisely correspond neither to the previously published data, nor to CZ-COICOP.
Employees and wages
The data refer to the numbers of employees registered by businesses. They include persons with employment contracts for jobs, members of cooperatives with employment contracts and persons in duty status.
The data on the number of employees and on average wages do not include persons in public office (e.g. deputies, senators, full-time councillors), judges, females on maternity leave, persons on parental leave (unless they have contract of employment at the same time), apprentices, persons employed by companies under contracts of services or for work, and employees of businesses not measured statistically.
An average gross monthly wage is the ratio of wages excluding other personnel expenses per employee per month. Included in the wages are basic wages and salaries, payments additional to wage or salary, direct remuneration and bonuses, remuneration for being on call to work, and other wage or salary components charged to be paid to employees in a given period. They are gross wages i.e., before premiums for general health insurance and social security, income tax advances of natural persons, and other statutory deductions or deductions agreed with the employee.
In the 1st quarter of 2003, the circle of the units measured was enlarged to also include the parts of the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of the Interior not covered before. This change has been reflected into the annual data from 1993 and subsequent years and into the quarterly data starting from the first quarter of 1998.
Administrative data sources (the Czech Social Security Administration) have been used since the 1st quarter of 2003 to find out the activity/inactivity and size of businesses; the indices (corresponding period of the previous year = 100) for individual quarters of 2003 are related to the quarters of 2002 adjusted according to the same methodology.
The data listed in the tables come from the processed quarterly statistical questionnaires and refer
a) in the business sphere to all employees on the books of businesses :
- - with 25+ employees from 1990 (in industry, trade, hotels and restaurants with 100+ employees in 1995 and 1996)
- with 20+ employees from 1997, including employees of private unincorporated entrepreneurs,
- in financial intermediation irrespective of the number of employees;
Unemployment
The source of data on the numbers of job applicants out of work, who are registered by the labour offices, is the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs.
The source of data on the numbers of unemployed job applicants registered by the labour offices is the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs of the CR.
The registered unemployment rate is derived as the ratio in which by the end of the 2nd quarter the numerator includes the number of job applicants registered by the labour offices as at the last day of the reference period and the denominator includes labour force, i.e.
a) the number of employed persons in all sectors of the national economy with the only or main job, plus women on maternity leave and child-care leave (from enterprise survey) plus the number of unemployed job applicants registered by the labour offices as at the end of the reporting period (by the end of the 1st quarter of 1994), or
b) the number of employed persons as obtained by the LFSS plus the number of unemployed job applicants registered by the labour offices as at the last day of the reference period (from the 2nd quarter of 1994 to the end of 1996), or
c) the number of employed persons as obtained by the LFSS plus the number of unemployed job applicants registered by the labour offices (all annual moving averages). Unlike the previous periods, women on child-care leave are excluded from employment (starting with the 1st quarter of 1997).
In the 3rd quarter of 2004, the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs adopted a methodological change which consists in a different inclusion of some groups of persons in both the numerator and the denominator of the ratio mentioned above. The numerator now contains the number of available unemployed job applicants, including Czech and EU (EEA) citizens – they are unemployed persons registered as at the and of period who are ready to take up a job immediately. The denominator includes labour force – i.e. the number of the employed as established by the LFSS plus the number of EU (EEA) citizens plus the number of foreigners from third countries, holding valid work permit or trade certificate, plus the number of available unemployed job applicants (all moving annual averages).
Selected indicators from LFSS
Data in the time series are processed using unified methodology corresponding to the valid definitions of Eurostat and recommendations of the ILO. All the figures for 1997 and previous years are deannualised to quarterly periods. Since 1998 the data have been measured for calendar quarters already.
The category of the employed in the national economy excludes women on child-care leave or persons on parental leave. On the other hand, the employed persons include both regular and temporary members of the armed forces (the last named only till year 2004).
The category of the unemployed corresponds with the ILO definition - i.e., in addition to persons who meet the three standard conditions for being classified as unemployed, the category also includes persons who have found a job, but will take it up later.
External trade
The source of information on external trade are data collected by customs authorities. Starting from processing of the January 2004 data, data collection and the first check are carried out by the Directorate General of Customs (DGC), whereas the Czech Statistical Office is in charge of further data processing, checks and publishing.
In compliance with the binding regulations of the EU, the measurement of data on exports and imports is governed by Customs Act No. 13/1993 Sb., as amended; by Decree No. 199/2004 Sb., on trade with third countries implementing certain provisions of the customs act and repealing certain decrees regulating exemptions from import duty and the non-preferential origin of goods (by the Ministry of Finance of the CR) as amended, effective since 1 May 2004. Intrastat, is governed by Decree No. 563/2005 Sb., on statistics of exported and imported goods and on the way of sharing data on trade with the other Member States of the European Communities amending decree No. 201/ 2005 Sb. which came into effect on 1 January 2007.
External trade statistics is made up of the sum of intra - Community trade (trade with the EU Member States) and trade with third countries. Data on goods traded between Member States of the Communities are supplied by reporting units to the customs office on the Intrastat questionnaire, with information on dispatches of goods or arrivals of goods. Data on imported and exported goods in trade with third countries are given in a Single Administrative Document (SAD).
SITC, Rev. 4 was accepted by the United Nations Statistical Commission in March 2006 and became effective on 1 January 2007. SITC, Rev. 4, retains the overall structure of SITC, Rev. 3, and consists of the same number of sections, divisions and groups. The changes made were at the level of basic headings and some subgroups.
Business Register
The table listing numbers of units kept in the Business Register is compiled from data kept in the Register as of respective date.
The Business Register keeps records of legal persons, government departments - accounting units, and natural persons with the status of entrepreneur.
A business that is economically active according to statistical surveys or administrative sources is considered to be a statistical enterprise-type unit (see Regulations No. 696/1993 and 2 186/1993).
The indicator „Private entrepreneurs, total“ includes (i) by the end of 1991: natural persons authorised to do business according to the Private Enterprise of Citizens Act 105/90 Sb., (ii) from 1992: natural persons with licence and (iii) from the 3rd quarter of 1991: self-employed farmers (or agricultural entrepreneurs – natural persons).
The indicator „Business companies and partnerships“ includes general commercial partnerships, limited liability companies, limited partnerships, share limited partnerships (up to 1992) and joint-stock companies. The indicator „Cooperatives“ also includes cooperative enterprises. State-owned enterprises in liquidation are from 1994 excluded from state-owned enterprises.
The reason for the drop in the number of units in the 1st quarter of 1994 is the completion of the re-registration of entrepreneurs according to the Trade Act.
Agriculture
The total sales of animals for slaughter, excluding poultry, include sales of cattle, pigs, sheep, goat and horses, all for slaughter (between 1998 and 2002 only sales of cattle and pigs for slaughter were included).
Since 2003, in compliance with the EU harmonisation requirements for reporting, the populations of cattle and pigs are not measured in the third quarters.
Industry
Industrial production index (IPI) measures the output of industrial branches and the industry in total, adjusted for price variations. It is a basic indicator of business cycle statistics of industry. Calculation is based mainly on sales of own products and services converted into constant prices. For selected branches (section C, sub-section DG, section E) the development is measured by physical volumes of product representatives. The index is primarily computed as a monthly base index, now, at average month of the year 2000 for CZ-NACE two-digit division. In aggregation to higher level the weights derived from the value added structure in the base year are used (aggregations to the level of subsection, section, main industrial groupings and the industry in total). From base indices the y-o-y indices and cumulations in time (quarterly, semi-annual and annual cumulations) are derived.
By the end of the year 2005, the IPI was formed purely on the product representative sample. Beginning from the Press Release for January 2006, the industrial production index including the back conversion of time series is processed in compliance with the above methodology as published also in the Press Release of 10 March 2006 (http://www.czso.cz/csu/redakce.nsf/i/zmena_metodiky_indexu_prumyslove_produkce).
Construction
Construction output includes construction work done by enterprises with prevailing construction activity (CZ-NACE = 45). Included are enterprises with 20 or more employees (up to 1996 with 25 or more; with the exception of 1991 100 or more employees). Data on them are collected by reports, while construction work for enterprises up to 19 employees is estimated.
The index is based on constant prices of 2000.
Housing construction
Dwelling refers to one or more rooms designed for living by the building authority, which can serve as independent housing units for this purpose. The number of dwellings includes also separate rooms in hostels, home for students and young workers and rooms in boarding houses for single people which are not managed by local authorities.
Dwellings started are, from 2006, dwellings in buildings the construction of which was permitted in the reference period by a building permit granted and, from 2007, by a building permit or building notification irrespective of whether or not these dwellings were completed in the reference period. For this purpose, the building refers to a family house, multi-dwelling building and extensions to them, community care service home and boarding house, non-residential building (tied dwellings usually outside residential buildings) and any non-residential space whose conversion provides a new dwelling.
Completed dwellings embrace dwellings approved for the use, in compliance with Act No. 183/2006 Sb. (Building Act) as amended, by the permit granted by a respective building authority by the end of the reference period in compliance with Section 122.
Dwellings under construction are those dwellings the construction of which was started by the end of the reported period (irrespective of whether in the reported period or in preceding periods) but not completed by the end of the reported period.
Building permits
The building notifications is understood a permit for building of simple constructions under Section 104 para 2 leter a) to d) of Act No. 183/2006 Sb., on Town and Country Planning and on the Building Code (Building Act).
The building permit lays down binding conditions for the building and use of a construction within the meaning of Section 115 of Act No. 183/2006 Sb., on Town and Country Planning and on the Building Code (Building Act).
The numbers of building notifications and building permits are added up by building authorities and regarded as permitted constructions.
The approximate value of constructions includes total costs, incl. technology (at current prices), of preparing, implementing and putting a construction into use.
Sales in the segment of motor vehicles, retail trade, hotels and restaurants
Sales in the segment of motor vehicles, retail trade, hotels and restaurants include total
sales, including VAT, of goods for resale, own goods, and services, as measured by monthly survey on a fixed sample of enterprises.
The released indicator is the index of these sales in retail trade, hotels and restaurants compared to the corresponding period of the previous year. According to the CZ-NACE classification, the following divisions are involved:
- 50 - Sales, maintenance and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles; retail sale of automotive fuel
52 - Retail trade including repair of personal and household goods
55 - Hotels and restaurants
Sale, maintenance and repair of motor vehicles - CZ-NACE 50.1 to 50.4
Retail sale of automotive fuel - CZ-NACE 50.5
Retail sale in non-specialised stores with food, beverages or tobacco predominating - CZ-NACE 52.11
Retail sale of food, beverages and tobacco in specialised stores - CZ-NACE 52.2
Retail sale of other goods than food - CZ-NACE 52.12, 52.3 to 52.6
Restaurants, bars, canteens and catering - CZ-NACE 55.3 to 55.5
Hotel, camping sites and other provision of short-stay accommodation - CZ-NACE 55.1 to 55.2
Index at current prices: corresponding period of the previous year = 100
Index at constant prices: corresponding period of the previous year = 100
(price index related to the 2000 average was used for deflation)
Revision
During the processing of the February data, the data for January will be revised. If necessary, the data to be processed on the first month following the publication of quarterly data are revised, e.g. while processing the data for April, the data for January to March will be revised. Final data will be published next June, at the latest, upon processing the data for all months of the reference year.
Transport
The indicator “Transport of goods” refers to the actual weight of goods in terms of metric tonnes transported on the basis of a contract of carriage.
The indicator “National transport” – refers to loading and unloading of transported goods in terms of metric tonnes carried out within the Czech Republic.
The indicator “Passenger transport” refers to persons transported by public passenger transport over a given period. It does not include persons transported by public city transport.
Guests at collective accommodation establishments
Data on guests at collective tourist accommodation establishments are based on the regular sample survey organized by the CZSO. Until 2002 (including) the collective accommodation establishments were included in the survey on the basis of a random 30% selection from the Register of accommodation establishments. A monthly obligation to report was set for the respondents and results were published quarterly. Since 2003 the survey covers all collective establishments on the basis of area sampling. The survey is divided into a monthly survey, which covers selected units and quarterly survey covering the rest of the collective accommodation establishments. Data on guests is the total of processed data from submitted reports and imputed data of accommodation establishments that failed to report.
Collective accommodation establishments – an establishment with at least five rooms or ten beds used for the purpose of tourism that is offering temporary accommodation to guests (including children) for the purpose of a holyday, trip, spa treatment, business trip, training, course, congress, symposium, children’s school in nature, summer and winter children camps, etc.
Number of guests – a guest in an accommodation establishment is a person (personnel and owner living in the establishments are not included) who used the services of an accommodation establishment for their temporary stay. The guest can use the services of the accommodation establishment for the purpose of a holyday, trip, spa treatment, business trip, training, course, congress, symposium, children’s school in nature, summer and winter children camps. In some recreational centres and training centres of enterprises (trade unions) a guest is every person which used the establishment for their temporary stay from the above mentioned reasons whether it concerns employees of the enterprise (e.g. members of the trade unions), their family members or persons foreign to the enterprise. In health resorts a guest is a person, which undergoes spa treatment regardless the way of payment of the treatment and the complexness, etc. Guests are not considered to be persons, which use the services of an accommodation establishment for temporary stay for the purpose of employment or regular study (if the period exceeded 1 year).
Number of overnight stays – the number of overnight stays of guest at an accommodation establishment in an observed period.
Other market services
Other market services include data for businesses and unincorporated entrepreneurs whose prevailing activity classifies them to the following CZ-NACE divisions:
- 70 Real estate activities
71 Renting of machinery and equipment without operator and of personal and household goods
72 Computer and related activities
73 Research and development
74 Other business activities
75 Public administration and defence; compulsory social security
80 Education
85 Health and social work
90 Sewage and refuse disposal, sanitation and similar activities
91 Activities of membership organisations, n.e.c.
92 Recreational, cultural and sporting activities
93 Other service activities
The indicator „Total sales“ comprises sales of own goods and services and of goods for resale.
The indicator „Total employment“ is measured as the average registered number of employees who have contract with the employer, irrespective of their working hours. Excluded are women on maternity leave and child-care leave, persons on military service, apprentices and students on training, and persons working under contracts for work or service.
The indicator „Average gross monthly wage“ is the average gross wage of actual persons, i.e. irrespective of hours worked.
Social security and social assistance benefits, social security contributions
In June 2007, based on the Eurostat foreign mission recommendation, a change of the contents of social contributions and social benefits took place. From 2004 household social benefits (D.62) include means designed for health insurance of persons for whom the insurance is paid by the state (children, students, pensioners, etc.). The amount of the above contribution is then shown as household expenditure (S.14) on health insurance and as income of health insurance companies (S1314) within D.61. This second imputation results from the need to settle the relationship to social benefits.
In relation with the above these payments made by the state between the central government (S.1311) and social security funds (S.1314) were excluded from the value of transfers within the sector of the general government (D.73).
The change of the concept of social contributions and benefits in the time series from 1995 will be realized not earlier than during the national accounts revision.
Social security and social assistance benefits paid out to households are current, regular and irregular money and in-kind payments (transfers) to citizens, which are paid from social security funds, including benefits from central government budgets to so-called non-civilian components and benefits from abroad. They also include payments made from supplementary insurance schemes managed by insurance companies (on the basis of legal claims), non-statutory benefits provided by employers, government and private non-profit institutions providing services to the population. Social security benefits and social assistance benefits are split into:
Pension insurance benefits which consist of old-age pensions, disability pensions, orphan's and other pensions (including pensions based on supplementary pension insurance).
Sickness insurance benefits which include sickness benefits, family member care benefits, maternity benefits, maternity and pregnancy compensation benefits, and sickness insurance benefits not elsewhere classified.
Unemployment benefits are paid to job applicants registered by the employment offices, usually for a period of six months. If out of work for a longer period of time, job applicants are materially secured in compliance with social security regulations.
State social support benefits included child benefits, social benefit, birth grant, parental benefit, providing-for benefit, foster care benefit and housing benefit.
Other benefits and assistance (excl. in-kind benefits) plus imputed state contribution for health insurance of persons for whom the health insurance is paid by the state include also benefits paid by local authorities in the framework of their schemes of social care for senior citizens, family and population. They also include social security benefits provided outside the government schemes of social security, i.e. social support paid by the employer (e.g. from the social fund).
Social benefits in kind include mainly the value of health establishments performances at level paid by health insurance companies (96 to 98% of benefits in kind), state social support benefits or contributions to transport, funeral and housing, and other state social support benefits and mainly benefits provided in the framework of schemes for handicapped persons and schemes of social care for senior citizens.
Contributions to social security for the household sector refer to all (both statutory and non-statutory) payments made directly or indirectly to social security benefit providers, i.e. to social security funds (incl. the unemployment fund), health insurance companies and pension funds. They have been measured and included since the year of their enactment.
Social contributions of employers include mandatory social insurance (so that the state can pay pensions, sickness benefits, incl. contribution to the unemployment fund), health and mandatory insurance against loss or damage at occupational accidents or occupational disease. Voluntary social contributions contain the contributions of employers to supplementary pension insurance, voluntary contributions to health and life insurance.
The payments of these contributions create the citizen’s right to social security benefits and the provision of medical care in favour of the policy holder or the user of compensation (e.g. the claims of family members or heirs in case of the policy holder’s death).
The contributions are paid by employers on behalf of their employees, by employees (in form of deductions from their wages), by self-employed or non-employed persons on their own behalf, and by the state (on behalf of retired non-working persons, children and students).
